Artificial photosynthesis boosted by four-charge storage molecule
Source: interestingengineering
Author: @IntEngineering
Published: 8/26/2025
To read the full content, please visit the original article.
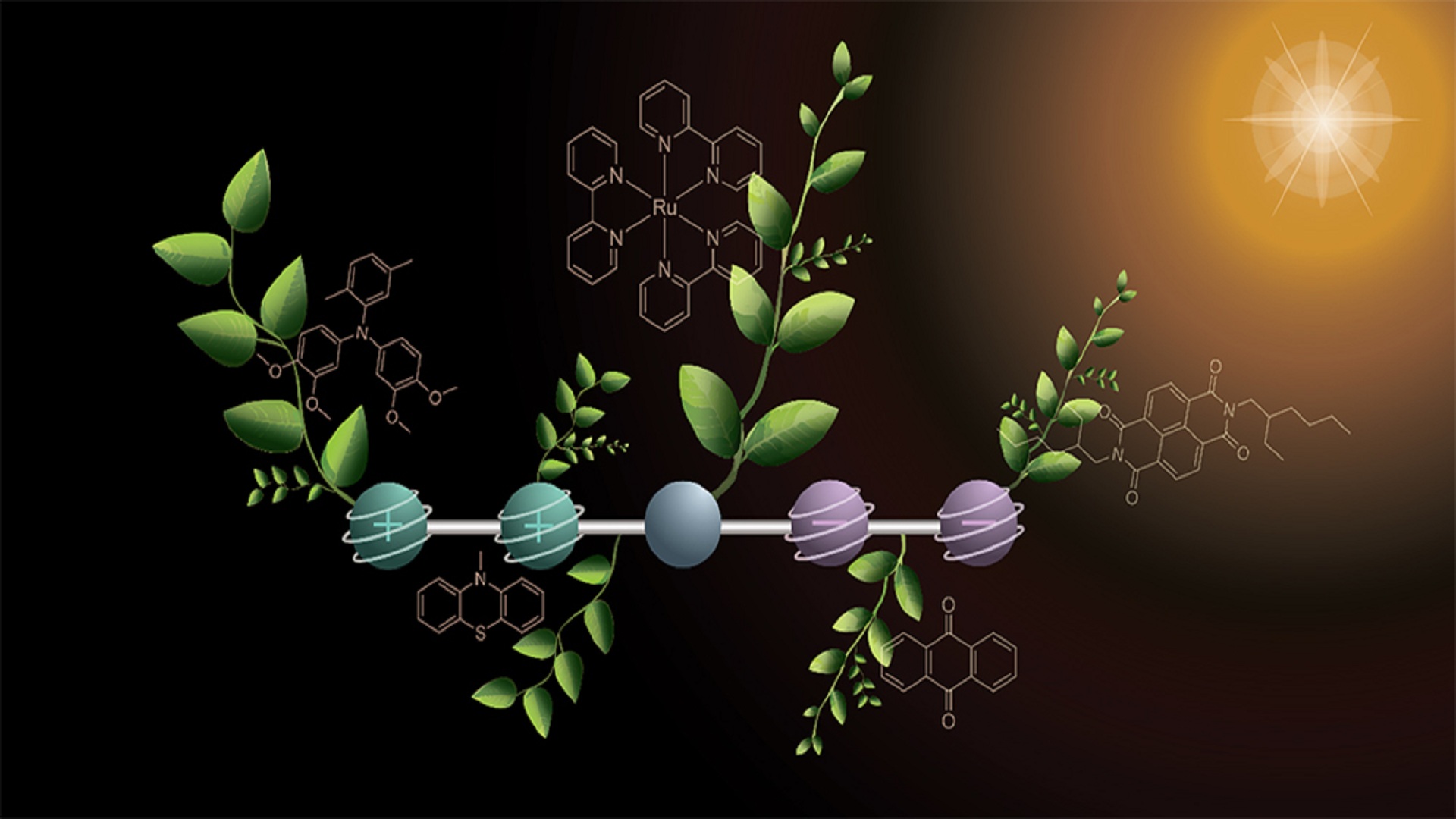
Read original articleScientists at the University of Basel have developed a custom-built molecule capable of storing four electrical charges generated by sunlight, marking a significant advancement in artificial photosynthesis. This molecule, composed of five linked components, mimics natural photosynthesis by temporarily holding two positive and two negative charges. The design allows the molecule to absorb sunlight and sequentially transfer electrons, enabling the accumulation and stabilization of multiple charges—a critical requirement for driving complex solar fuel production reactions such as water splitting into hydrogen and oxygen.
Using two flashes of light, the researchers demonstrated the molecule’s ability to generate and maintain these charges under light intensities approaching natural sunlight, a notable improvement over previous methods that required intense laser light. The stable storage of multiple charges opens the door for further chemical reactions needed to synthesize carbon-neutral fuels like hydrogen, methanol, or synthetic petrol. While not yet a complete artificial photosynthesis system, this molecule represents a vital building block toward practical, sustainable solar fuel technologies, bringing the scientific community closer to harnessing solar energy
Tags
energyartificial-photosynthesissolar-fuelscharge-storagecarbon-neutral-energymolecular-engineeringrenewable-energy