Water vapor can double conductivity for better fuel cells, study finds
Source: interestingengineering
Author: @IntEngineering
Published: 8/30/2025
To read the full content, please visit the original article.
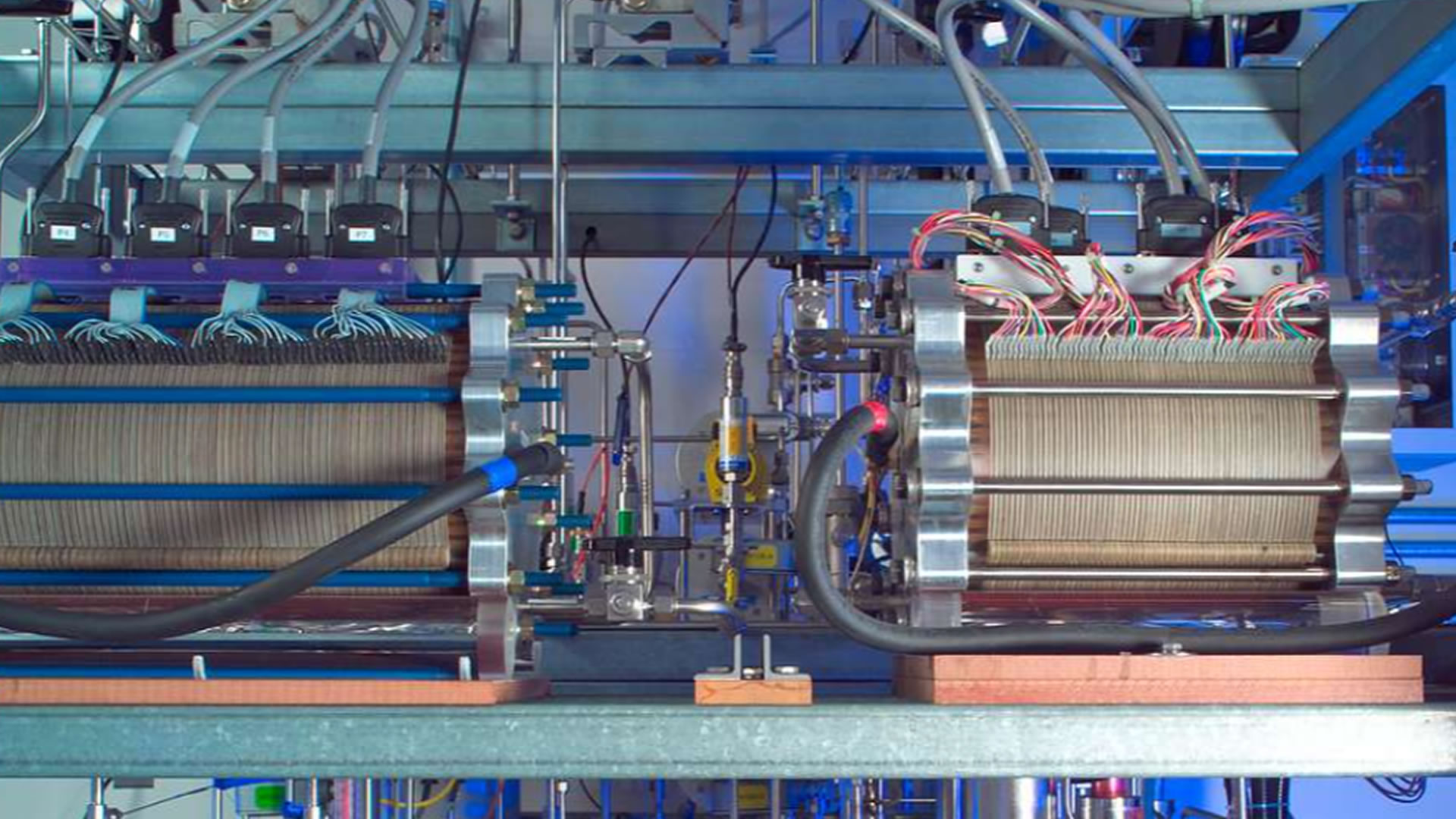
Read original articleResearchers at the Institute of Science in Tokyo have discovered that introducing water vapor significantly enhances the oxygen ion conductivity of a ceramic material called barium–niobium–molybdenum oxide (Ba₇Nb₄MoO₂₀), which is promising for solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs). At 932°F (500°C), exposure to water vapor more than doubled the material’s oxide ion conductivity, improving ion flow without relying on protons as charge carriers. This effect occurs because water absorption adds interstitial oxygen ions that facilitate the movement of oxide ions through the crystal lattice by forming and breaking small dimer units, thereby easing ion mobility.
This breakthrough addresses a major challenge in SOFC technology, which traditionally requires very high operating temperatures (up to 1,832°F/1,000°C) that cause rapid material degradation and high costs. By enabling efficient ion conduction at lower temperatures around 932°F, the new material could lead to longer-lasting, cheaper fuel cells
Tags
energyfuel-cellssolid-oxide-fuel-cellsceramicsion-conductivitymaterials-scienceclean-energy